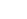
Stainless steel hex bolts are widely used in construction, marine, automotive, and industrial applications due to their strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. However, many people mistakenly believe that stainless steel is completely immune to rust. While it is highly resistant, stainless steel can still corrode under certain conditions — especially in wet or humid environments where moisture, salt, and pollutants are present. Understanding how to prevent rust formation is key to ensuring the long-term performance of stainless steel hex bolts.
1. Choose the Right Stainless Steel Grade
The first and most important step is selecting the proper stainless steel grade. Not all stainless steels perform equally in wet conditions. For general use, 304 stainless steel offers good corrosion resistance. However, in high-moisture or salt-rich environments like coastal areas or marine applications, 316 stainless steel is a better choice. It contains molybdenum, which significantly enhances corrosion resistance, especially against chloride-induced pitting and crevice corrosion.
2. Avoid Surface Contamination
Even high-grade stainless steel can rust if its surface becomes contaminated. Iron particles, dust, or debris from carbon steel tools or environments can embed into the stainless steel and initiate corrosion. To prevent this:
Always use dedicated tools for stainless steel during installation.
Keep the bolts clean and free from dirt, grease, and metal filings.
Wipe down bolts after handling, especially in industrial or workshop environments.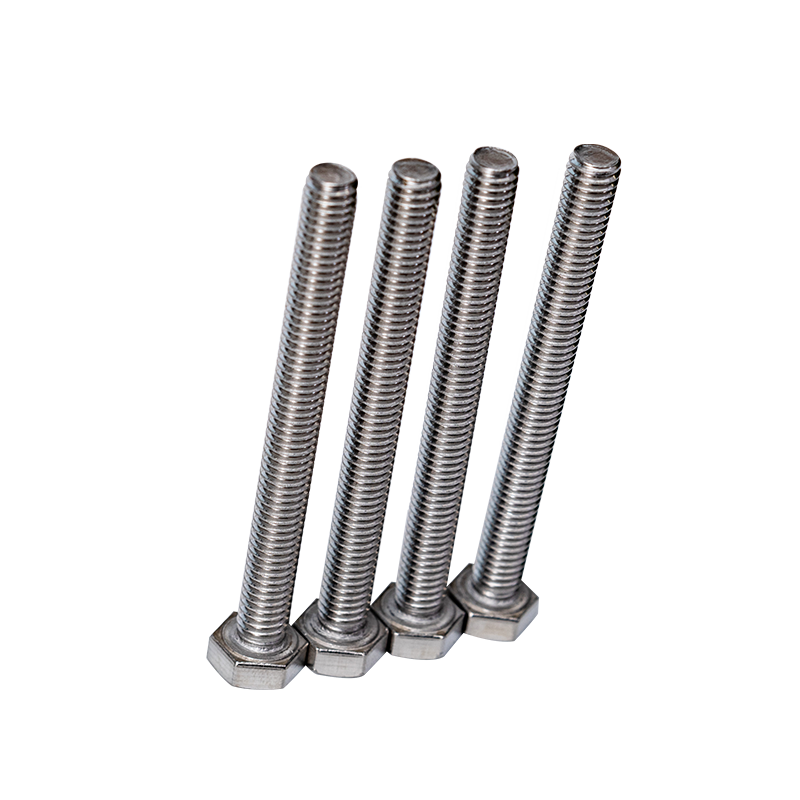
3. Proper Storage Before Installation
Before being installed, stainless steel hex bolts should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated place, away from corrosive chemicals or wet surfaces. Avoid stacking bolts in a way that traps moisture or allows water to pool. Covering them with plastic sheets in humid areas may trap moisture and promote rusting. Instead, use breathable materials or store them in sealed containers with desiccants.
4. Protective Coatings and Lubricants
Applying a protective coating or anti-corrosion lubricant can greatly enhance the rust resistance of stainless steel bolts. Options include:
Dry film lubricants
Corrosion-inhibiting sprays
Passivation treatments, which remove free iron from the surface and enhance the chromium oxide protective layer
In aggressive environments, electropolishing can also be used to create an ultra-smooth surface that reduces corrosion risks.
5. Proper Installation Techniques
Improper installation can expose stainless steel bolts to corrosion risks. Ensure that:
Threads are not over-tightened, which can damage the passive film.
Bolts are not in contact with dissimilar metals that may cause galvanic corrosion, especially in wet environments.
Gaskets, washers, or insulating sleeves are used when necessary to separate different metals.
6. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Even with good installation and material selection, ongoing exposure to moisture can lead to corrosion over time. Routine inspections help identify early signs of corrosion before they become serious. If any surface discoloration or rust appears:
Clean it immediately using non-metallic brushes or mild cleaners.
Use citric or nitric acid-based passivation solutions to restore corrosion resistance.
Stainless steel hex bolts are strong and corrosion-resistant, but not invincible. In wet environments, rust prevention depends on choosing the right grade of stainless steel, avoiding surface contamination, using protective coatings, and performing regular maintenance. By following these best practices, you can greatly extend the life of your stainless steel fasteners and ensure safe, long-lasting installations in even the harshest conditions.



 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى italiano
italiano
 No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province  +86-17315333748(Wechat)
+86-17315333748(Wechat)
 +86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)
+86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)