Introduction to Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
Hex bolts—characterized by their six-sided heads—are one of the most widely used types of fasteners across industries. Known for their strength and ease of use with a wrench or socket, they’re commonly found in construction, machinery, automotive systems, and household applications. Among the various types available, stainless steel hex bolts stand out due to their superior durability and resistance to corrosion.
Stainless steel hex bolts are favored in environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures is common. Their aesthetic appeal, longevity, and reliability make them suitable for both functional and decorative purposes. Whether securing a structural beam, assembling marine equipment, or maintaining sanitary conditions in food processing facilities, these bolts offer consistent performance and peace of mind.
Understanding Stainless Steel
Before diving deeper into the features of stainless steel hex bolts, it's important to understand the material they are made from—stainless steel.
What Is Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is a steel alloy primarily composed of iron, carbon, and at least 10.5% chromium by mass. It may also contain other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and manganese, depending on the desired properties. The presence of chromium is what gives stainless steel its defining trait: corrosion resistance. When exposed to oxygen, chromium forms a thin, invisible layer of chromium oxide on the surface that protects the underlying metal from rust and corrosion.
Common Grades of Stainless Steel
There are several grades of stainless steel used in manufacturing hex bolts, with 304 and 316 being the most prevalent:
304 Stainless Steel: Often considered the “standard” grade, 304 stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength. It is suitable for general-purpose use and is widely used in architecture, food equipment, and household hardware.
316 Stainless Steel: Contains additional molybdenum, which improves resistance to chlorides and harsh chemical environments. This makes it ideal for marine applications and industries where chemicals and salt are prevalent.
Other Grades: Depending on the application, you may also encounter grades like 410 (hardenable stainless steel with higher strength but less corrosion resistance) or 18-8 (an austenitic stainless steel with 18% chromium and 8% nickel, often used interchangeably with 304).
Why Choose Stainless Steel?
The main advantages of stainless steel in bolt manufacturing include:
Corrosion Resistance: Unmatched protection against rust, especially in outdoor, marine, and chemical settings.
Aesthetic Appeal: Bright, clean finish that maintains its appearance over time.
Strength and Durability: High tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it suitable for load-bearing applications.
Low Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep compared to coated or painted fasteners.
Key Properties of Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
When selecting fasteners, understanding the material's key characteristics is crucial. Stainless steel hex bolts offer a range of properties that make them ideal for both commercial and industrial uses.
1. Corrosion Resistance
Arguably the most significant advantage of stainless steel hex bolts is their outstanding corrosion resistance. Thanks to the chromium content, these bolts naturally form a passive oxide layer that protects them from moisture and oxidation.
Marine Environments: In saltwater conditions, 316 stainless steel hex bolts perform exceptionally well due to their resistance to chloride-induced corrosion.
Chemical Exposure: In industrial settings where bolts are exposed to acids, solvents, or alkaline compounds, stainless steel resists degradation and maintains structural integrity.
This resistance not only extends the life of the fastener but also reduces maintenance costs and replacement frequency.
2. Tensile Strength
Stainless steel hex bolts are engineered to withstand high tensile loads, which makes them suitable for demanding structural applications.
304 Grade typically has a tensile strength of around 70,000–85,000 psi, while
316 Grade can range slightly higher depending on the manufacturing process.
High tensile strength ensures that bolts can hold heavy materials together without snapping or deforming under stress.
3. Temperature Resistance
These bolts retain their strength and resist oxidation at both high and low temperatures.
In high-temperature environments (up to 870°C for some grades), stainless steel maintains its mechanical properties.
In cold climates, stainless steel doesn’t become brittle, making it a reliable option for outdoor use in freezing conditions.
This makes them suitable for use in boilers, engines, refrigeration systems, and even aerospace applications.
4. Durability
Stainless steel hex bolts are known for their exceptional durability. Unlike galvanized or zinc-coated bolts that may wear over time, stainless steel offers long-term performance in harsh conditions without flaking or corroding.
Resistant to mechanical wear: Great for applications with vibration or movement.
Non-reactive: Ideal for sanitary or chemical-sensitive settings like food manufacturing or pharmaceutical production.
5. Magnetic Properties (Optional Consideration)
While most stainless steels are non-magnetic, some cold-worked or hardened types may exhibit mild magnetic properties. This aspect may or may not be critical depending on your application but is worth noting when selecting bolts for electronic or sensitive environments.
Types and Standards of Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
Stainless steel hex bolts come in a wide variety of types, dimensions, and specifications, tailored to meet the needs of diverse industries and environments. Understanding these classifications helps ensure you're selecting the right fastener for your specific application.
Types of Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
Although all hex bolts share a six-sided head design, they differ in several key areas:
1. Fully Threaded vs. Partially Threaded
Fully Threaded Hex Bolts have threads running the entire length of the shank. These are ideal for situations requiring a greater grip length, such as clamping two thin materials together.
Partially Threaded Hex Bolts have an unthreaded shoulder near the head, which provides better shear strength and alignment for structural applications.
2. Heavy Hex Bolts
These bolts have a larger head and thicker body than standard hex bolts. They're designed for heavy-duty structural applications, particularly in construction and steel fabrication.
3. Hex Cap Screws
Often confused with standard hex bolts, hex cap screws are manufactured to tighter tolerances, especially in terms of thread length and head dimensions. They are commonly used in precision machinery and automotive work.
Head and Drive Types
While the classic hex head is standard, variations exist based on installation needs:
Standard Hex Head: Installed using a wrench or socket.
Flanged Hex Head: Includes a built-in washer under the head to distribute load and reduce surface damage.
Socket Head: Features a recessed hex drive, allowing installation in tight spaces using an Allen key.
Some hex bolts also include features such as serrated flanges to prevent loosening from vibration.
International Standards and Classifications
To ensure compatibility and quality, stainless steel hex bolts are manufactured according to recognized standards. Common standards include:
ANSI (American National Standards Institute): Defines dimensions, material composition, and strength grades in the U.S.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Provides global standards for bolt sizes, thread pitch, and tolerance.
DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung): German standards often used in European engineering.
For example:
DIN 931: Partially threaded hex bolt.
DIN 933: Fully threaded hex bolt.
ISO 4014/4017: International equivalents to the above DIN standards.
Understanding these standards helps ensure correct interchangeability, especially for projects that involve international suppliers or specifications.
Sizes and Dimensions
Stainless steel hex bolts are available in a wide range of sizes, typically measured in:
Diameter (e.g., M6, M8, M10 for metric; 1/4", 3/8", 1/2" for imperial)
Length (measured from the flat of the head to the end of the bolt)
Thread Pitch (distance between threads, e.g., coarse vs. fine thread)
When choosing the size, it's critical to match the bolt to the application’s load-bearing needs and the materials being joined.
Applications of Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
Stainless steel hex bolts are valued across multiple industries for their strength, reliability, and resistance to corrosion. Here’s a breakdown of the most common sectors where they are applied:
1. Construction Industry
In building and infrastructure projects, stainless steel hex bolts are used to join structural elements like beams, supports, and panels. Their strength and resistance to environmental elements make them ideal for:
Bridges
High-rise buildings
Outdoor metal frameworks
Reinforced concrete anchors
Their ability to endure both mechanical stress and exposure to moisture makes them preferable over carbon steel in many long-term or outdoor projects.
2. Automotive Sector
Hex bolts are crucial in assembling vehicle components where vibration resistance and durability are key. Stainless steel hex bolts are often used in:
Engine compartments
Chassis assemblies
Exhaust systems (due to high temperature and corrosion exposure)
While stainless bolts aren’t always used in high-torque engine applications (due to cost and potential galling issues), they are preferred in parts that need longevity and weather resistance.
3. Marine Environments
One of the most common uses of 316 stainless steel hex bolts is in marine applications. Their superior resistance to saltwater corrosion makes them ideal for:
Boat hulls and decks
Dock construction
Underwater pipelines
Coastal infrastructure
Stainless steel bolts ensure that salt-laden air and direct water exposure don't compromise the structural integrity of marine equipment.
4. Food and Beverage Processing
Hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount in this industry. Stainless steel hex bolts are widely used in food production and packaging machinery because:
They don’t rust or contaminate food.
They withstand frequent wash-downs and sterilization with chemical cleaners.
They meet FDA and NSF sanitary standards.
Common uses include assembling conveyor belts, mixers, storage tanks, and processing lines.
5. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
In facilities where exposure to acids, solvents, and other harsh chemicals is routine, stainless steel’s chemical resistance is critical. Stainless hex bolts are used in:
Piping systems
Reaction vessels
Storage tanks
Clean rooms
316 stainless steel, in particular, offers excellent resistance to chemical attack and is commonly found in chemical plants and laboratories.
6. Renewable Energy and Utilities
Wind turbines, solar panel mounts, and hydroelectric systems use stainless steel bolts due to their long-term reliability in outdoor conditions. Their resistance to UV exposure, rain, and thermal cycling makes them ideal for:
Solar farm structures
Wind turbine towers
Water treatment facilities
7. Home Improvement and DIY Projects
On a smaller scale, stainless steel hex bolts are popular among hobbyists and homeowners for:
Outdoor furniture assembly
Deck construction
Pergolas and garden structures
Bicycle or motorbike repairs
Their clean finish and rust-resistance make them an attractive and practical option for both indoor and outdoor use.
Selecting the Right Stainless Steel Hex Bolt
Choosing the right stainless steel hex bolt is not just a matter of size or length—it involves evaluating the environment, mechanical requirements, material compatibility, and standards. Making the wrong choice could lead to premature failure, corrosion, or structural weaknesses. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what to consider:
1. Consider the Environment
Environmental conditions are perhaps the most critical factor when selecting stainless steel hex bolts. Different grades of stainless steel perform better in specific settings:
Indoor/General Use: 304 stainless steel is typically sufficient for dry indoor environments or light outdoor use with minimal exposure to moisture or chemicals.
Coastal or Marine Areas: Use 316 stainless steel due to its high resistance to salt spray and chlorides.
High-Humidity Zones: Environments like greenhouses, basements, or tunnels can benefit from 316-grade fasteners to prevent rusting.
Chemical Exposure: In chemical plants or labs, bolts may be exposed to acids, solvents, or alkaline substances—again, 316 or higher alloy grades are recommended.
Long-tail keywords like "best stainless steel hex bolts for marine use" reflect these considerations and are useful for product pages or SEO-focused guides.
2. Load Requirements
Understanding the mechanical stress the bolt will be subjected to is crucial. Important load factors include:
Tensile Load: The force trying to pull the bolt apart.
Shear Load: The force acting across the diameter of the bolt.
Clamping Force: How tightly the bolt pulls the materials together.
Choosing a bolt that lacks sufficient tensile or shear strength can result in deformation or failure. Refer to the bolt’s tensile strength rating (usually in PSI or MPa) and ensure it matches your design calculations.
For example, Grade A2-70 bolts (common for 304 stainless steel) have a minimum tensile strength of 700 MPa and are suitable for medium-load applications.
3. Size and Dimensions
Selecting the correct size means considering:
Bolt diameter (e.g., M6, M10, 1/4”, 3/8”)
Length: Measured from under the head to the end of the thread.
Thread pitch: Coarse threads are faster to assemble and more tolerant of wear, while fine threads provide better tension control.
If you’re unsure of the size, use a thread gauge or refer to standardized dimension charts (ANSI, DIN, ISO) to ensure compatibility with existing holes and nuts.
4. Grade Selection
Stainless steel hex bolts are often categorized by mechanical grade in addition to the steel grade:
A2-70: Most common; general-purpose applications.
A4-80: Higher strength and better corrosion resistance (marine/chemical use).
B8 / B8M: ASTM classifications used in pressure vessels and piping systems.
Always match the grade to both the mechanical and environmental needs of your project.
Installation Best Practices
Even the best stainless steel hex bolt can fail if not installed properly. Following proper installation procedures ensures safety, reliability, and long-term performance.
1. Preparing the Joint
Before installation, clean all surfaces of the components being fastened:
Remove debris, dust, oils, and oxidation from both bolt and material surfaces.
Ensure bolt holes are aligned and not oversized, which can reduce clamping force.
Use flat washers when needed to distribute the load and prevent marring.
For high-precision or safety-critical applications, it's essential to follow pre-load procedures and component alignment specs.
2. Torque Specifications and Why They Matter
Applying the correct torque is essential to ensure the bolt stays secure without over-stressing the threads or causing stretching.
Under-tightening can lead to loosening over time due to vibration.
Over-tightening may cause thread stripping, bolt fatigue, or even joint failure.
Always refer to the manufacturer's torque chart based on the bolt grade, size, and lubrication condition (dry or lubricated).
Use a calibrated torque wrench for consistency.
3. Using Appropriate Tools
Use high-quality tools that match the bolt’s head size and drive type:
Wrenches and sockets for standard hex heads.
Allen keys or hex bits for recessed heads.
Anti-seize lubricant to prevent galling or thread damage, especially on larger stainless bolts where friction is a concern.
Never substitute with an ill-fitting tool as it may round off the head or strip the thread.
Maintenance and Care
Stainless steel bolts are low-maintenance, but they’re not completely immune to environmental impact. A regular maintenance schedule ensures longevity and performance.
1. Regular Inspection Tips
Inspect bolted connections periodically, especially in harsh or load-bearing environments:
Check for surface rust, pitting, or discoloration.
Look for loose fasteners due to vibration or material fatigue.
Ensure there’s no sign of galling (threads seizing or binding).
Inspections are particularly important in safety-critical structures such as bridges, handrails, or marine decks.
2. Cleaning Methods to Prevent Corrosion
While stainless steel resists corrosion, it still requires occasional cleaning to maintain its passive oxide layer:
Use warm water and a mild detergent to remove dirt and contaminants.
For tougher stains or salt buildup, use a non-abrasive brush or specialized stainless steel cleaner.
Avoid harsh acids or chloride-containing cleaners, which can accelerate corrosion.
For commercial settings, implement a scheduled cleaning protocol for all exposed bolts.
3. When to Replace Bolts
Replace stainless steel hex bolts if you observe:
Thread damage or wear that affects torque or engagement.
Severe corrosion, especially near the head or threads.
Fatigue cracking, often appearing near the head-shank transition.
Galling or signs of cold welding between bolt and nut, making future removal difficult.
Document all replacements in maintenance logs, particularly in regulated industries (like food or chemical processing).
Common Problems and Solutions
Although stainless steel hex bolts are known for their strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, they’re not entirely problem-proof. Understanding the most frequent issues and how to prevent them can help ensure longer-lasting, safer connections.
1. Thread Stripping
Cause: Thread stripping occurs when excessive torque is applied or when the nut/bolt materials are mismatched in hardness. Over-tightening and cross-threading are typical culprits.
Solution:
Always follow torque guidelines for the bolt grade and size.
Use matching materials (e.g., stainless steel nut with stainless steel bolt).
Avoid power tools for small bolts where control over torque is limited.
Use thread lubricants or anti-seize compounds to reduce friction and prevent binding.
2. Corrosion Issues
Despite their high resistance, stainless steel hex bolts can still suffer from certain types of corrosion under the right (or wrong) conditions:
Pitting Corrosion: Often caused by chloride exposure, particularly in coastal areas.
Crevice Corrosion: Occurs in narrow gaps where oxygen can’t reach, such as under washers or between joined surfaces.
Galvanic Corrosion: Happens when stainless steel is in contact with a dissimilar metal in a conductive environment (e.g., aluminum or carbon steel in salty air).
Prevention:
Choose the right grade: 316 stainless steel is superior for chloride-heavy or chemical environments.
Avoid pairing stainless steel with dissimilar metals unless using insulation (e.g., plastic washers or isolation sleeves).
Ensure good drainage and airflow to prevent water entrapment in crevices.
3. Seizing (Galling)
One of the most common issues with stainless steel bolts is galling, where friction during tightening causes the threads to lock together permanently. This is especially prevalent in stainless-on-stainless connections due to the metal’s tendency to form microscopic welds under pressure.
Prevention:
Apply a high-quality anti-seize lubricant on the threads before installation.
Avoid using power tools that may cause rapid heating or excess friction.
Use hardened or coated nuts when frequent disassembly is expected.
Tighten slowly and evenly, especially on larger bolts.
If galling occurs, the fastener often must be cut or drilled out, which can be time-consuming and damaging to surrounding components.
4. Loosening Under Vibration
While stainless steel hex bolts are strong, they can still loosen over time in high-vibration environments (e.g., machinery, vehicles, or industrial equipment).
Solutions:
Use locking nuts, nylon-insert lock nuts, or thread-locking adhesives.
Add spring washers, split washers, or serrated flange heads to maintain tension.
Periodically inspect and re-torque critical fasteners.
Where to Buy Stainless Steel Hex Bolts
With many different sizes, grades, and specifications, it’s important to buy stainless steel hex bolts from reputable sources to ensure you’re getting high-quality, standard-compliant products.
1. Reputable Online Suppliers
Online shopping offers convenience, especially for bulk orders or hard-to-find specifications. Reliable suppliers include:
McMaster-Carr – Wide range of stainless steel fasteners, clearly labeled specs and materials.
Grainger – Industrial supply leader with strong inventory for stainless steel bolts and hardware.
Fastenal – Nationwide presence with both online ordering and physical stores.
Bolt Depot – User-friendly interface, perfect for DIYers or small businesses.
Amazon (Industrial Section) – Offers a range of fasteners, but ensure you verify seller reputation and material certifications.
Tips for Buying Online:
Double-check product grade, thread pitch, length, and diameter before ordering.
Look for suppliers that provide material certificates or compliance with standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN).
Consider shipping costs and lead times—especially for international orders.
Use SEO keywords like "where to buy stainless steel hex bolts online" to guide searchers directly to your product listings or supplier comparisons.
2. Local Hardware Stores and Industrial Distributors
In-store purchasing allows you to physically inspect the fasteners and get immediate access:
Home Depot, Lowe’s, and other major retailers usually stock common sizes of stainless hex bolts for general-purpose use.
Specialty fastener shops often carry more specific or high-grade bolts (e.g., A4-80 or DIN 933).
Benefits of Buying In-Store:
Instant availability.
No risk of ordering the wrong size if you can bring a sample.
Access to in-person advice or custom orders.
However, local availability may be limited compared to online inventories, especially for specialty bolts.
Stainless steel hex bolts are essential components in everything from small household repairs to large-scale industrial installations. Their popularity stems from a unique combination of features:
High tensile strength
Excellent corrosion resistance
Durability in extreme temperatures and environments
Versatility across industries
Understanding the differences in steel grades, standards, and applications is key to choosing the right hex bolt for your needs. Whether you're working on a marine project, assembling machinery, or upgrading food processing equipment, there’s a stainless steel hex bolt perfectly suited for the job.
Final Tips:
Choose 316 stainless steel for the best corrosion resistance.
Use anti-seize compounds to avoid thread galling.
Apply correct torque to maintain joint integrity.
Inspect and maintain fasteners periodically for long-lasting performance.
Buy from trusted suppliers and insist on standardized, certified materials.
By following this guide and considering both technical and environmental factors, you can ensure long-lasting, safe, and reliable fastening solutions.
Stainless steel hex bolts are among the most widely used fasteners in construction, manufacturing, automotive, marine, and industrial applications. Known for their corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and durability, these bolts offer long-term reliability even in harsh environments.
Hex bolts feature a six-sided head and are designed for use with a wrench or socket. When made from stainless steel, they offer significant advantages, especially in environments prone to moisture, chemicals, or salt exposure. Two of the most common stainless steel grades are 304 (A2) and 316 (A4). While 304 is suitable for general use, 316 offers superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine or chemical applications.
Choosing the right stainless steel hex bolt involves more than just size. Key factors include the operating environment, load requirements, bolt grade, and thread specifications. Proper torque application, matching nut and bolt materials, and using anti-seize lubricant are also critical to prevent issues such as thread stripping, galling, and loosening under vibration.
Bolts must be installed with care, following best practices such as cleaning joint surfaces, applying the correct torque, and using appropriate tools. Regular maintenance—including inspection, cleaning, and timely replacement—extends their lifespan and ensures safety. Although stainless steel is resistant to corrosion, it still requires upkeep to prevent issues like crevice or galvanic corrosion.
Common problems such as seizing, rust formation, or vibration-induced loosening can be avoided through material selection, surface treatments, and the use of locking mechanisms. For sourcing, buyers can choose from reputable online suppliers or local distributors, with online platforms offering broader selection and technical details.
Stainless steel hex bolts are essential fasteners in many critical systems. By understanding their properties, proper selection criteria, and maintenance needs, users can maximize the bolt’s performance and avoid costly failures. Whether you're working in construction, marine engineering, or food processing, stainless steel hex bolts offer a balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and long-term value.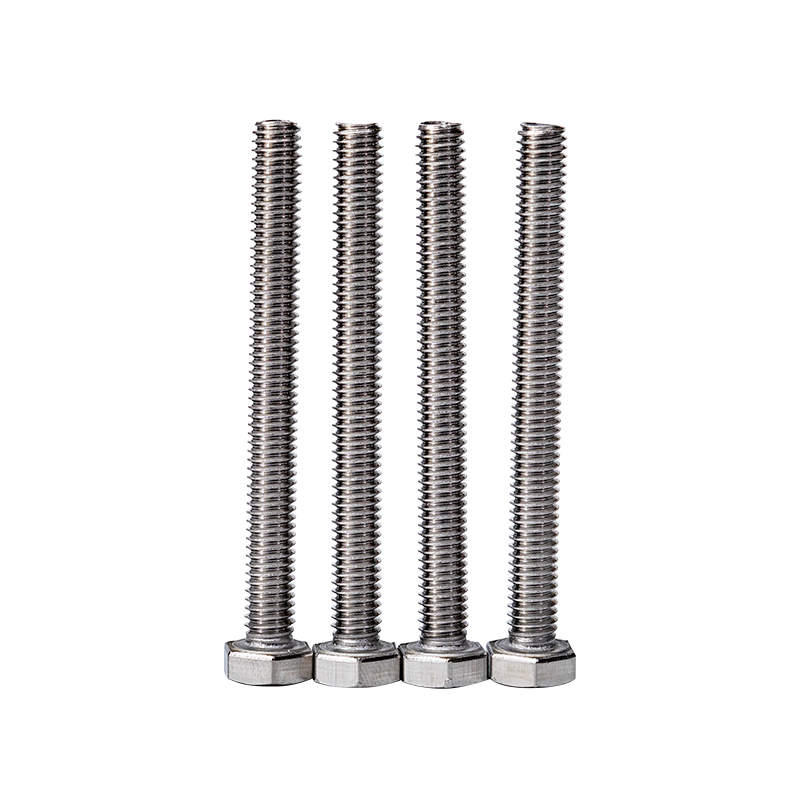



 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى italiano
italiano
 No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province  +86-17315333748(Wechat)
+86-17315333748(Wechat)
 +86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)
+86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)