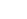
Introduction to Stainless Steel Spring Washers
Stainless steel spring washers are widely used in mechanical assemblies to maintain tension and prevent loosening of fasteners. Their unique design allows them to exert a spring force between the fastener head and the substrate, compensating for vibration and thermal expansion. While they are durable and resistant to corrosion, assembly practices significantly impact their performance and lifespan. Improper handling or installation can lead to deformation, cracking, or loss of spring tension, affecting the overall integrity of the assembly.
Common Causes of Damage During Assembly
Several factors can contribute to the damage of stainless steel spring washers during installation. These include over-tightening, misalignment of the fastener, use of incorrect tools, and handling errors. Each of these can compromise the washer’s mechanical properties, leading to premature failure.
Over-Tightening
Excessive torque during assembly is one of the most common causes of spring washer damage. When the applied force exceeds the washer’s elastic limit, it may permanently deform or lose its spring action. This can reduce the washer’s ability to maintain proper tension and prevent loosening, ultimately jeopardizing the stability of the entire assembly.
Misalignment of Fasteners
Misaligned screws or bolts place uneven stress on the spring washer. Instead of compressing uniformly, the washer may bend or experience localized stress points. Over time, these stress concentrations can lead to cracks or even breakage. Proper alignment is critical to ensuring the washer distributes force evenly and functions as intended.
Use of Inappropriate Tools
The tools used during assembly, such as wrenches or sockets, must match the fastener and washer specifications. Using worn-out or oversized tools can slip and damage the washer surface. Additionally, applying uneven pressure during tightening can lead to deformation or scratching, compromising corrosion resistance and mechanical integrity.
Handling and Storage Errors
Improper handling before installation is another factor. Dropping or stacking washers incorrectly can cause dents or scratches. Environmental factors such as moisture or chemical exposure during storage can also weaken the surface, making the washers more susceptible to damage during assembly.
Material Properties and Durability
The durability of stainless steel spring washers largely depends on the type of stainless steel used. Austenitic stainless steel, such as 304 or 316 grades, offers excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical strength. Martensitic stainless steels have higher hardness and better load-bearing capacity but are less corrosion-resistant. Understanding the material properties helps engineers select washers that withstand specific assembly conditions without deforming or cracking.
Elastic Limit and Fatigue Resistance
A washer’s elastic limit determines how much deformation it can withstand before permanent damage occurs. Spring washers are designed to operate within their elastic range to maintain tension. Repeated tightening and loosening cycles subject the washers to fatigue. High-quality stainless steel washers are engineered to resist fatigue, but improper assembly can exceed the material’s endurance, leading to failure.
Best Practices for Preventing Damage
To ensure stainless steel spring washers maintain performance, certain best practices should be followed during assembly.
Correct Torque Application
Always follow manufacturer-recommended torque values. Using a calibrated torque wrench helps apply consistent force without exceeding the washer’s elastic limit. This prevents permanent deformation and preserves spring tension.
Proper Alignment
Ensure fasteners are perpendicular to the substrate and aligned with the washer. Misalignment introduces uneven stress, which can damage the washer or fastener. Checking alignment before tightening is a simple step that significantly increases longevity.
Use of Appropriate Tools
Select tools that match the size and type of the fastener and washer. Avoid worn or damaged tools. This minimizes surface scratches and uneven compression, ensuring optimal performance.
Proper Handling and Storage
Store washers in a clean, dry environment to prevent surface corrosion. Handle them carefully to avoid scratches, dents, or bending. Organizing washers in trays or bins ensures that they remain in pristine condition prior to assembly.
Inspection and Quality Control
Regular inspection of stainless steel spring washers before and during assembly can prevent failures. Look for signs of deformation, surface scratches, or cracks. Using washers from reputable manufacturers ensures consistent quality and reduces the risk of assembly damage.
Visual Inspection
Check each washer for visible defects such as bends, scratches, or corrosion. Damaged washers should be discarded to prevent compromised performance in critical applications.
Batch Testing
Periodic mechanical testing of washers from production batches can detect deviations in hardness, thickness, or spring tension. Ensuring washers meet specifications reduces the likelihood of assembly-related damage.
Conclusion
Stainless steel spring washers are robust components designed to maintain tension and resist loosening in various assemblies. While they are not inherently fragile, improper handling, over-tightening, misalignment, and poor storage can lead to damage during installation. Following recommended torque values, proper alignment, correct tool usage, careful handling, and regular inspection are essential practices to ensure these washers function reliably. By understanding material properties and adopting best assembly practices, the risk of damage can be minimized, extending the life and performance of stainless steel spring washers in industrial applications.




 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى italiano
italiano
 No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province  +86-17315333748(Wechat)
+86-17315333748(Wechat)
 +86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)
+86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)