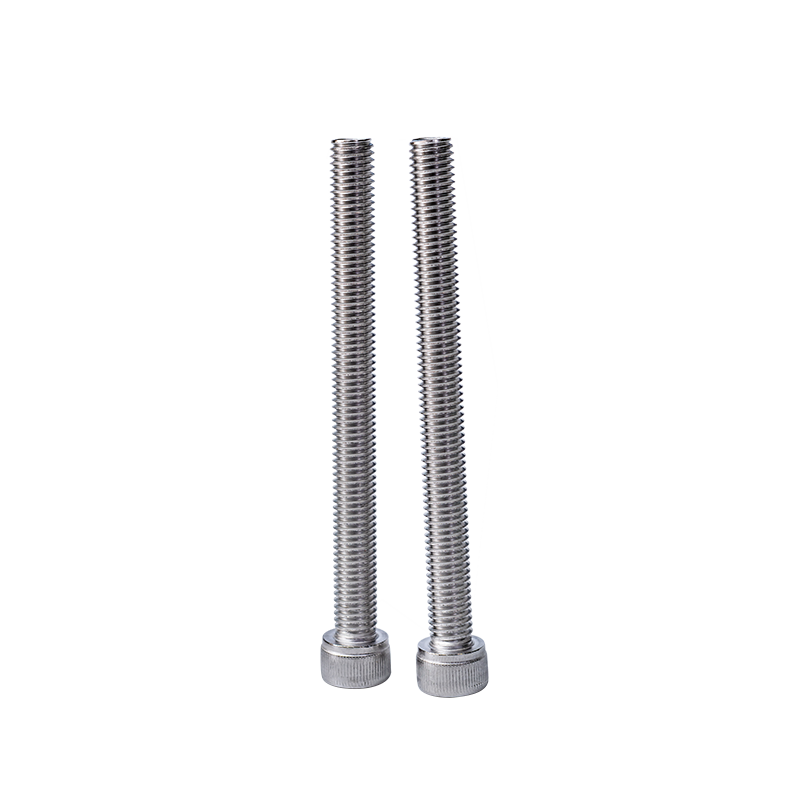
Introduction to Stainless Steel Allen Screws
Stainless steel Allen screws, also known as hex socket head screws, are widely used in mechanical, industrial, and DIY applications due to their strength, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. One of the most critical considerations for engineers and users is the load-bearing capacity of these screws. Understanding their strength characteristics ensures safe and reliable assembly of machinery, structures, and equipment.
Material Composition and Strength
The performance of stainless steel Allen screws is largely determined by their material composition. Key points include:
- Stainless Steel Grades: Common grades include 304, 316, and 410, each with varying corrosion resistance and tensile strength. 316 stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, while 410 stainless steel has higher hardness.
- Tensile Strength: Tensile strength is the maximum stress a screw can withstand before breaking. Standard stainless steel Allen screws can range from 500 MPa to over 1000 MPa, depending on grade and heat treatment.
- Yield Strength: Yield strength defines the stress at which a screw begins to deform permanently. Maintaining load below the yield ensures long-term reliability.
- Hardness: Hardness, often measured in Rockwell scale, affects wear resistance and screw longevity under repeated load.
Factors Affecting Load-Bearing Capacity
Several factors influence how much load a stainless steel Allen screw can safely bear:
- Screw Diameter: Larger diameters provide greater cross-sectional area, increasing load capacity.
- Thread Length and Pitch: Longer engagement with the mating material improves holding power. Finer threads distribute load more evenly.
- Material and Grade: Higher-grade stainless steel or heat-treated screws sustain higher loads without deformation.
- Installation Torque: Correct torque ensures proper clamping force without overstressing the screw.
- Environmental Factors: Corrosion, temperature, and vibration can reduce the effective load-bearing capacity over time.
Calculating Load Capacity
The load-bearing capacity of an Allen screw can be estimated using tensile strength and cross-sectional area:
- Tensile Load Formula: Load = Tensile Strength × Cross-Sectional Area
- Example: A 10mm diameter M10 Allen screw made of 304 stainless steel with tensile strength 700 MPa has a cross-sectional area of 58 mm². Maximum tensile load = 700 MPa × 58 mm² ≈ 40,600 N.
- Factor of Safety: Engineers usually apply a factor of safety (2–4) to ensure long-term reliability, reducing working load to 10,000–20,000 N in this example.
Comparison by Screw Size and Grade
Different sizes and grades of stainless steel Allen screws offer varying load capacities. The table below provides approximate tensile loads for common sizes:
| Screw Size | Material Grade | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Approx. Max Load (N) |
| M6 | 304 | 500 | 13,000 |
| M8 | 304 | 700 | 35,000 |
| M10 | 316 | 700 | 40,000 |
| M12 | 410 | 1000 | 100,000 |
| M16 | 410 | 1000 | 160,000 |
Applications in High-Load Environments
Stainless steel Allen screws are suitable for a wide range of applications where strong mechanical fastening is required:
- Industrial machinery and equipment assemblies
- Automotive and aerospace components
- Structural connections in metal frameworks
- Outdoor and marine equipment where corrosion resistance is critical
- Precision machinery and robotics requiring reliable torque retention
Installation Considerations
Proper installation is key to achieving the maximum load-bearing capacity:
- Torque Specifications: Applying correct torque prevents under-tightening (looseness) or over-tightening (thread stripping).
- Thread Engagement: Ensure full engagement of threads for optimal clamping force.
- Use of Locking Mechanisms: Lock washers or thread-lock compounds help maintain load under vibration.
- Surface Preparation: Clean mating surfaces prevent uneven stress distribution and premature failure.
Maintenance and Longevity
Maintaining stainless steel Allen screws enhances their lifespan and load-bearing reliability:
- Inspect screws periodically for corrosion, wear, or loosening.
- Reapply thread-locking compounds if necessary to prevent loosening under vibration.
- Replace damaged or worn screws immediately to maintain structural integrity.
- Store spare screws in dry environments to prevent corrosion before use.
Conclusion
Stainless steel Allen screws offer excellent load-bearing capacity, corrosion resistance, and long-term reliability, making them ideal for industrial, mechanical, and structural applications. Their maximum load depends on screw diameter, material grade, thread engagement, and installation quality. By understanding these factors, engineers and users can select the right screw for each application and ensure safe, durable, and high-performance assemblies. Proper installation, maintenance, and periodic inspection further enhance the strength and longevity of these versatile fasteners.




 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى italiano
italiano
 No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province  +86-17315333748(Wechat)
+86-17315333748(Wechat)
 +86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)
+86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)