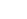
Stainless Steel Hexagon Flange Nuts Provide Superior Load Distribution and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel hexagon flange nuts integrate a built-in washer into the nut body, eliminating the need for a separate flat washer while distributing clamping force over a larger surface area. This design reduces the risk of material deformation, loosening from vibration, and surface damage—especially in soft substrates like aluminum or composites. Made from corrosion-resistant stainless steel alloys such as 304 (A2) or 316 (A4), these fasteners are ideal for harsh environments including marine, chemical processing, and outdoor infrastructure. According to a 2025 Fastener Industry Report, flange nuts account for 22% of all specialty nut sales in North America, with stainless steel variants growing at 9% annually due to demand in renewable energy and food-grade equipment.
Material Grades and Mechanical Properties
The performance of stainless steel hex flange nuts hinges on their alloy composition. The two most common grades are:
- A2 (304 Stainless): Offers excellent general corrosion resistance, suitable for indoor and mild outdoor use. Typical tensile strength: 700 MPa.
- A4 (316 Stainless): Contains 2–3% molybdenum for enhanced resistance to chlorides and acids—critical in marine, pharmaceutical, and coastal applications. Tensile strength: 800 MPa.
Both meet ISO 3506 and ASTM F593 standards for mechanical and dimensional compliance. Unlike carbon steel equivalents, they do not require plating, reducing long-term maintenance costs and environmental impact.
Key Advantages Over Standard Hex Nuts
The integrated flange delivers three critical engineering benefits:
- Increased Bearing Surface: Reduces stress concentration on thin or brittle materials, preventing pull-through or cracking.
- Vibration Resistance: Many flange nuts feature serrated undersides that act as lock washers, resisting rotation in dynamic assemblies.
- Faster Assembly: Eliminates separate washer handling, cutting installation time by up to 15% in high-volume production lines.
These advantages make them indispensable in automotive exhaust systems, solar panel frames, and food processing machinery where reliability and hygiene are non-negotiable.
Dimensional Standards and Sizing
| Thread Size (M) | Flange Diameter (mm) | Height (mm) | Wrench Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 14.2 | 5.0 | 10 |
| M8 | 17.6 | 6.5 | 13 |
| M10 | 21.0 | 8.0 | 16 |
All dimensions comply with ISO 4161, ensuring interchangeability across global supply chains.
Critical Applications Across Industries
Stainless steel hex flange nuts are specified wherever joint integrity and environmental resistance matter. In wind turbine nacelles, A4-grade flange nuts secure electrical enclosures exposed to salt spray. In food and beverage plants, their smooth, crevice-free surfaces meet FDA and EHEDG hygiene standards. Automotive manufacturers use them in fuel rail assemblies due to resistance to ethanol blends. A notable example: Tesla’s Model Y rear subframe uses M12 stainless flange nuts to mount suspension components, reducing galvanic corrosion risk when paired with aluminum chassis parts.

Installation Best Practices and Torque Guidelines
Proper torque is essential to avoid galling—a common issue with stainless steel fasteners due to adhesive wear during tightening. Recommended practices include:
- Applying anti-seize lubricant (e.g., nickel-based) to threads in high-load or high-temperature applications
- Using calibrated torque wrenches—never impact drivers—to prevent thread stripping
- Following manufacturer torque specs; e.g., M8 A2 flange nut: 18–22 Nm dry, 14–17 Nm lubricated
Galling can increase disassembly torque by up to 300%, leading to seized joints—making controlled installation critical.
Cost vs. Lifetime Value Analysis
While stainless steel hex flange nuts cost 2–3 times more than zinc-plated carbon steel equivalents, their total cost of ownership is often lower. In a 2024 study of offshore platform maintenance, structures using A4 flange nuts required 60% fewer fastener replacements over a 10-year period compared to coated steel. Additionally, they eliminate rework from rust staining on adjacent surfaces—a frequent issue in architectural glazing systems. For mission-critical or hard-to-access assemblies, the premium is justified by reduced downtime and lifecycle reliability.
Future Trends and Smart Fastening Integration
Innovations are expanding the role of stainless flange nuts beyond passive fastening. Embedded RFID tags now allow digital tracking of torque history and maintenance cycles in aerospace and rail applications. Meanwhile, additive manufacturing enables custom flange geometries for weight-sensitive electric vehicle components. As industries push toward predictive maintenance and circular design, these nuts—already durable, traceable, and recyclable—will remain foundational. For engineers prioritizing longevity, safety, and sustainability, stainless steel hexagon flange nuts are not just a component—they’re a strategic choice.



 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى italiano
italiano
 No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province  +86-17315333748(Wechat)
+86-17315333748(Wechat)
 +86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)
+86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)