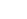
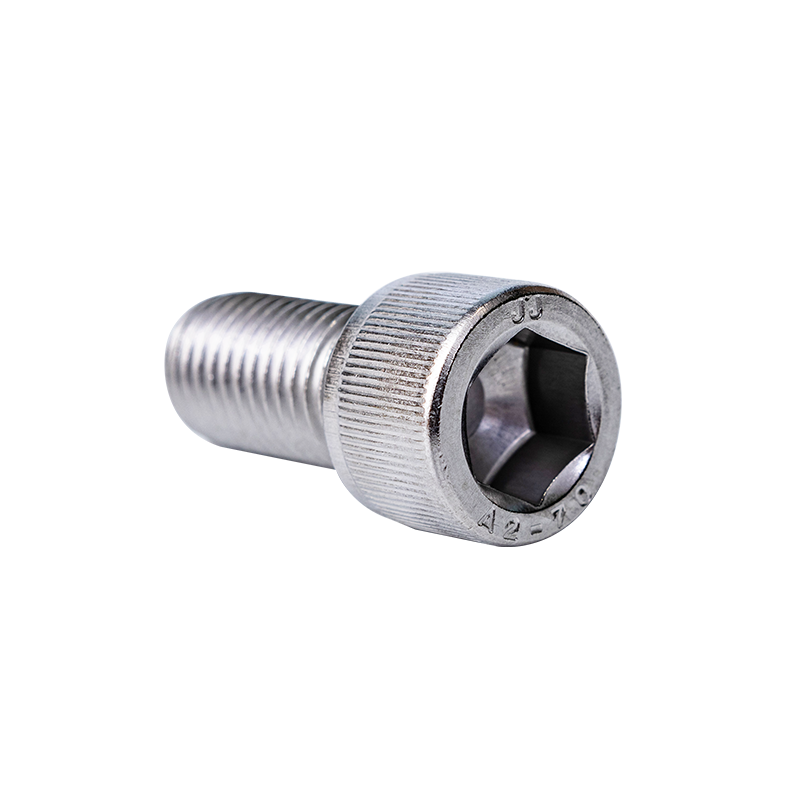
Stainless steel Allen screws, also known as hex socket screws or hex key screws, are widely used in industrial, commercial, and DIY applications due to their strength, corrosion resistance, and compact design. Understanding their common specifications is essential for selecting the right screw for a particular task. These specifications include dimensions, thread types, head styles, material grades, and strength ratings.
1. Dimensions: Diameter and Length
The two primary physical dimensions of stainless steel Allen screws are diameter and length. The diameter is typically measured in either metric (millimeters) or imperial (inches) units. Common metric diameters range from M2 to M20, with M3, M4, M5, M6, M8, and M10 being particularly popular for general applications. For imperial units, diameters often range from #2 to 3/4 inch.
The length of the screw is measured from the tip to the underside of the head. Standard lengths vary depending on diameter, with shorter screws used in compact assemblies and longer screws used for thicker materials or structural components. When selecting the screw length, it is important to account for material thickness and the depth of threaded holes to ensure proper fastening.
2. Thread Type and Pitch
Stainless steel Allen screws come in coarse and fine thread types. Coarse threads (e.g., M6x1.0, where “1.0” is the thread pitch in millimeters) are easier to install and remove and are commonly used in general applications. Fine threads (e.g., M6x0.75) offer higher precision and greater holding power, making them suitable for applications that require strong vibration resistance.
The thread pitch specifies the distance between threads. Correct selection of pitch is critical to ensure compatibility with nuts or threaded holes and to achieve proper clamping force without stripping threads. For imperial sizes, threads are measured in threads per inch (TPI), with typical coarse and fine designations.
3. Head Type
One defining feature of Allen screws is their hexagonal socket head, which allows tightening or loosening using an Allen key or hex wrench. However, there are multiple head styles, including:
Flat Head: Sits flush with the surface when fully installed; commonly used in countersunk holes.
Button Head: Rounded top, provides a smooth finish; used in applications requiring a softer appearance.
Socket Cap Head: Cylindrical and slightly taller, designed for high-strength applications.
Countersunk Head: Designed to fit flush in tapered holes; similar to flat head but with a precise angle.
Selecting the right head style depends on the application, whether aesthetics, strength, or flush mounting is a priority.

4. Drive Type
The drive type for Allen screws is a hex socket, but the size of the hex key needed varies according to the screw diameter. Common hex key sizes include 1.5mm, 2mm, 2.5mm, 3mm, 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, and 8mm for metric screws, and #0, #1, #2, #3, and 1/4 inch for imperial screws. Using the correct key size is essential to prevent stripping the socket and damaging the screw.
5. Material and Grade
Stainless steel Allen screws are made from various grades of stainless steel, with 304 and 316 being the most common.
304 Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance for general indoor and outdoor applications, moderate strength.
316 Stainless Steel: Contains molybdenum, providing superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments, including marine and chemical applications.
Other materials like 18-8 stainless steel or heat-treated stainless steel may be used for specialized applications requiring higher strength or wear resistance.
6. Strength and Hardness
Stainless steel Allen screws are classified by strength grades, which indicate the mechanical properties such as tensile strength and yield strength. For metric screws, common grades include:
A2-70: General-purpose stainless steel; 700 MPa tensile strength.
A2-80: Higher strength; 800 MPa tensile strength.
A4-70 and A4-80: Marine-grade stainless steel with superior corrosion resistance.
Imperial screws are often rated using ASTM or SAE standards. Selecting the correct strength grade is crucial for applications subjected to mechanical stress, vibration, or heavy loads.
7. Surface Finish and Coating
Most stainless steel Allen screws have a natural polished or passivated finish, which enhances corrosion resistance. Some may have additional coatings such as black oxide, zinc plating, or anti-galling treatment to reduce friction during installation. The finish may affect aesthetics, corrosion resistance, and wear performance, so it should be selected according to the working environment.
8. Special Features
Certain Allen screws include additional specifications, such as:
Fully threaded vs. partially threaded: Fully threaded screws are used where maximum engagement is required, while partially threaded screws leave an unthreaded shank for shear strength.
Self-tapping: Screws with cutting edges that create threads in softer materials without pre-drilling.
Vibration-resistant designs: Such as screws with nylon inserts or serrated heads to prevent loosening under vibration.
Stainless steel Allen screws are versatile fasteners, and understanding their common specifications ensures proper selection and reliable performance. Key specifications include diameter, length, thread type and pitch, head style, drive size, material grade, strength, surface finish, and any special features. Paying attention to these details helps prevent installation problems, ensures durability, and guarantees that the screws meet both functional and aesthetic requirements. Proper selection of stainless steel Allen screws ultimately leads to stronger assemblies, better corrosion resistance, and longer-lasting results in any project.



 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى italiano
italiano
 No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province
No. 2 Bridge, Chuangxin Road, Dainan Town, Xinghua City, Taizhou City, Jiangsu Province  +86-17315333748(Wechat)
+86-17315333748(Wechat)
 +86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)
+86-17315333748(Wechat/Whatsapp)